RESTORATIVE & SURGICAL DENTAL TREATMENTS
Gum Disease Treatment
Gum disease refers to conditions that affect the tissues supporting the teeth. The two main types are gingivitis and periodontitis.
Types of Gum Diseases
1. Gingivitis (Gum Inflammation)
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease, caused by plaque buildup that leads to gum inflammation and bleeding during brushing. At this point, no permanent bone or tissue damage has occurred, and with proper care, the condition is reversible. If untreated, it can progress to periodontitis.
2. Periodontitis
When gingivitis worsens, the gums and bone begin to pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that trap more bacteria. As the disease advances, these pockets deepen, causing loss of bone and gum tissue. Eventually, teeth may loosen and fall out. Periodontitis is the leading cause of tooth loss among adults.
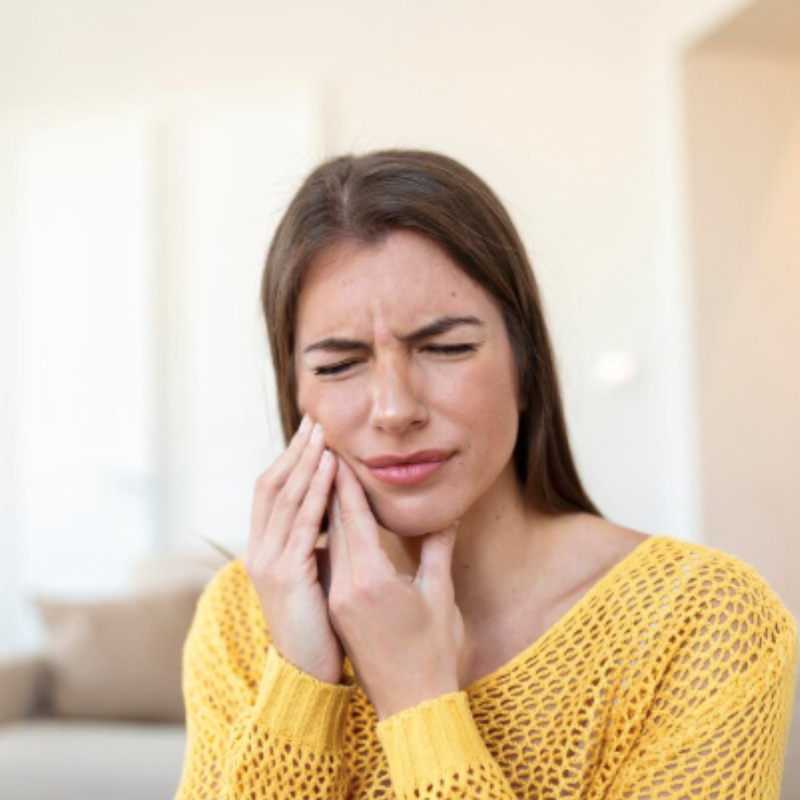


Common Risk Factors
While plaque is the primary cause, several factors can increase the risk of gum disease, including:
- Hormonal changes (e.g., pregnancy, puberty, menopause) that make gums more sensitive.
- Systemic illnesses such as diabetes, cancer, or HIV that weaken the immune system.
- Medications that reduce saliva flow or cause gum overgrowth.
- Smoking, which impairs gum healing.
- Poor oral hygiene, such as irregular brushing or flossing.
- Family history of gum problems.
Signs and Symptoms
Gum disease can progress quietly, but some warning signs include:
- Bleeding gums during brushing or flossing
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Persistent bad breath or unpleasant taste
- Gum recession (teeth appearing longer)
- Deep pockets forming between teeth and gums
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Changes in bite or denture fit
Even without visible symptoms, gum disease may still be present. Regular dental check-ups are essential for early detection and effective treatment.
Treatment for Gingivitis and Periodontitis
Stage 1 : Gum Analysis
Your dentist will examine your gums, take X-rays, and measure pocket depths to identify affected areas and determine the severity of the condition.
Stage 2: Cleaning
- Gingivitis: Treated through thorough scaling and polishing to remove plaque and tartar, paired with improved oral hygiene practices.
- Periodontitis: Requires deep cleaning below the gumline over one or two visits using ultrasonic tools. Severe cases may need gum or bone surgery (e.g., regeneration, grafting, pocket reduction) for full recovery.
Local anaesthesia may be provided to ensure comfort during the procedure.
Stage 3: Aftercare
Wait for numbness to wear off before eating. Mild swelling, bleeding, or sensitivity is normal and should subside within days. Take any prescribed antibiotics as directed.
Regular follow-up visits are essential to monitor healing and prevent relapse. Maintain proper daily oral care to keep gums healthy and disease-free.
Frequently Asked Question
How To Prevent Gum Disease?
To maintain healthy gums and prevent gum disease:
- Brush twice daily
- Floss at least once a day
- Schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings
- Manage diabetes effectively
- Avoid smoking
Is Polishing the Same as Tooth Whitening?
No. Polishing and stain removal only eliminate surface stains from coffee, tea, or smoking.
Tooth whitening, however, lightens the natural color of your teeth for a brighter appearance.
